
Digital Twin-Enabled Microfactory: Revolutionizing Smart Manufacturing
Harnessing Digital Twins to Transform Manufacturing Processes
NTT DATA, in collaboration with the Digital Twin Consortium, has introduced the Digital Twin-Enabled Microfactory(*1), a modular and scalable innovation for smart manufacturing. It integrates IoT, AI, real-time data, 3D visualization, and computer vision to optimize production. The system enables predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and enhances productivity. Backed by NTT DATA's global Innovation Center, the microfactory (*2) demonstrates how digital twins can transform manufacturing with flexibility, cost-efficiency, and operational reliability across a wide range of industrial applications.
Manufacturers everywhere are constantly under the pressures of increased productivity, improved efficiency, and sustainability along with cost savings and downtime reduction. NTT DATA, in response to these challenges and together with the Digital Twin Consortium (DTC), has launched the innovative Digital Twin-Enabled Microfactory(*3). It all shows how digital twins combined with innovative technologies bring practical advantages in smart manufacturing. This initiative is a direct result of the strategic investments made by NTT DATA's Innovation Center, a global structure committed to accelerating the adoption of emerging technologies across industries.
Strategic Innovation using Digital Twin Technology
The Digital Twin-Enabled Microfactory is a pioneering world-wide innovation initiative aimed at showcasing the potential of digital twins across smart manufacturing environments. Leveraging the architecture of the Digital Twin Consortium's Capabilities Periodic Table (CPT), the microfactory presents flexible and scalable solutions appropriate for a range of industry-use-cases.
Carlos Toro, Ph.D., Head of Data & Analytics at NTT DATA Chile, underlines the significance of this work: "Through this technology showcase, NTT DATA aims to channel our deep manufacturing knowledge into a modular, portable asset. It allows us to test and refine digital twin applications-especially when it comes to enhancing the reliability and consistency of robotic systems like the Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm (SCARA) manipulator."
Pietro Dicosta, Head of Digital Twin at NTT DATA Innovation Center, highlights its value from a global perspective: "Backed by our global Innovation Center, this initiative perfectly showcases the power of collaborative innovation. By bringing together cross-functional teams around the world and cutting-edge technologies, it creates a dynamic environment where ideas are transformed into scalable solutions with real-world impact."
Core Components of the Microfactory
IoT and Real-Time Data Integration
At the heart of the microfactory, are IoT sensors connected via IoT gateways to programmable logic controllers (PLCs). This setup enabled ongoing live data streaming - a crucial feature for monitoring and optimizing of production processes is required in near real time.
AI-Powered Predictive Capabilities
Artificial intelligence brings another layer of value by translating data into actionable insights. The system can anticipate issues before they become problems, thanks to AI-powered predictive maintenance protocols and anomaly detection-dramatically reducing unplanned downtime and optimizing resource usage.
Advanced Visualization and Remote Operations
With immersive 3D visualization and remote access features, the microfactory empowers operators to oversee production conditions in real-time, from virtually anywhere. Interactive dashboards and environmental telemetry provide deep insight without requiring a constant physical presence on the shop floor.
Computer Vision and Fault Detection
Fault detection is also elevated through computer vision technologies that quickly flag misalignments or anomalies during production. These real-time alerts trigger immediate responses, helping teams maintain smooth operations and prevent minor errors from escalating.
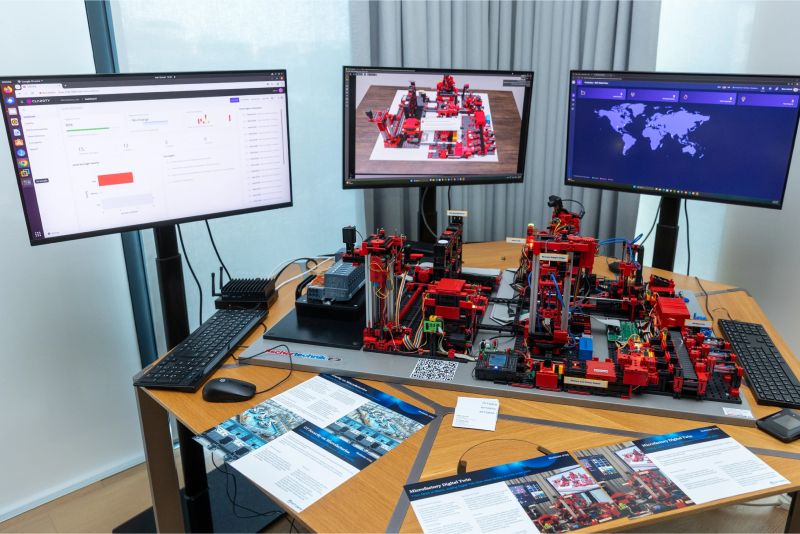

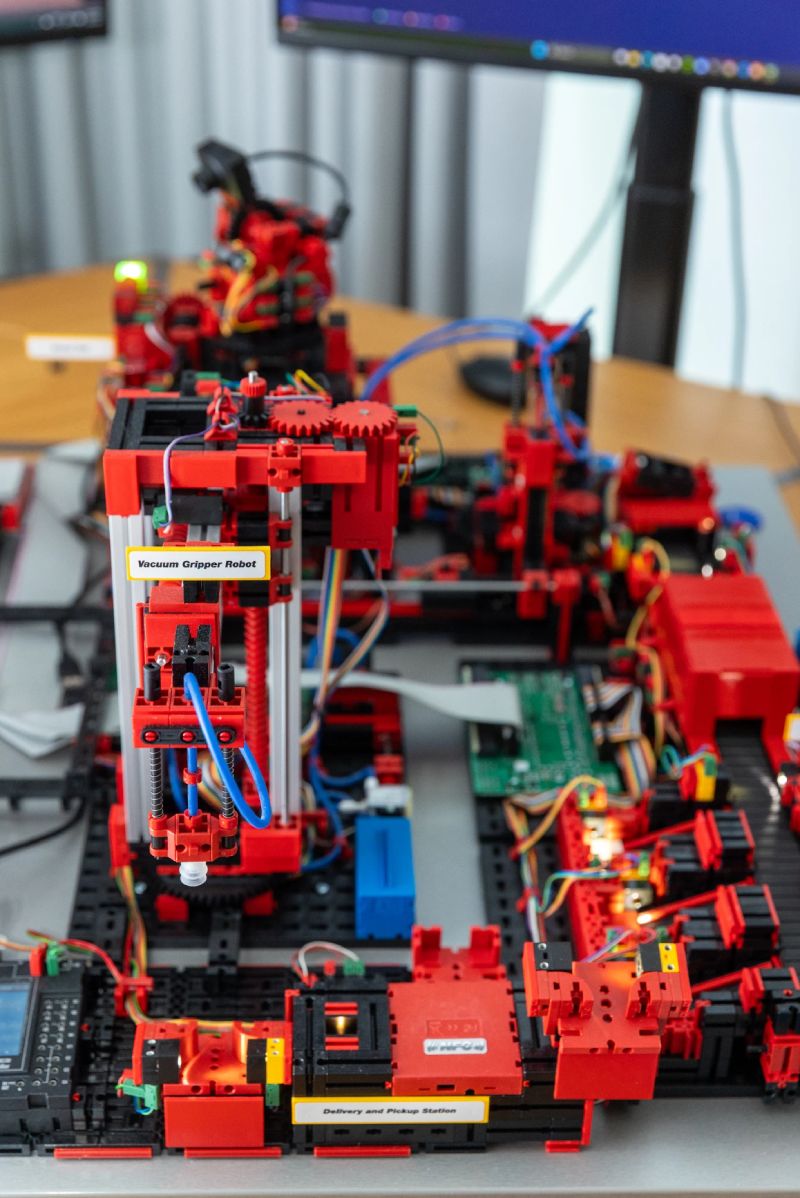
Tangible Impact and Industry Benefits
Adoption of the Digital Twin-Enabled Microfactory will result in several dramatic operational improvements, such as:
- Improved productivity and reduced downtime: By analyzing real-time information and predictive analytics, it brings a significant decrease in downtime, and thus, resulting in an outstanding increase in productivity.
- Lower maintenance costs: Good predictive maintenance provides cost savings with better uptime and extend the life of assets.
- Extended flexibility and scalability: Its composable modular design provides fast scalability and is adaptable to different industrial requirements and technology evolvements.
Conclusion
The Digital Twin-Enabled Microfactory marks an important milestone in the evolution of smart manufacturing, which was made possible thanks to the innovative partnership between NTT DATA and Digital Twin Consortium. The initiative combines IoT, AI and digital twin technologies to offer scalable, cutting-edge answers to sector-wide pressing issues.

Carlos Toro
Head of Data and Analytics
Carlos Toro is the Head of Data and Analytics at NTT DATA Chile and serves as an Ambassador for the Digital Twin Consortium. With a strong academic foundation - holding a degree in Mechanical Engineering, a master's in Automatic Control, and a PhD in Artificial Intelligence - he brings deep technical expertise and international experience. Prior to joining NTT DATA as Senior Manager of Digital Architecture, he led advanced manufacturing R&D initiatives in Spain and Singapore, where he worked closely with government agencies on national innovation strategies.

Pietro Dicosta
Head of Digital Twin & Smart Space
Pietro Dicosta leads the Smart Spaces and Digital Twin initiative within NTT DATA's Global Innovation Center. With over a decade of experience in innovation and a strong international background, he has held various strategic roles at NTT DATA. He began his career as a Research Fellow specializing in Big Data and has since contributed to numerous projects at the intersection of emerging technologies and applied research. His international collaborations include serving as a Visiting Scientist at both the MIT Media Lab in Boston and the NTT R&D Laboratories in Tokyo.
